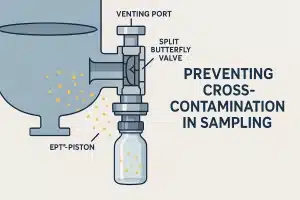
In a complex industrial environment, Industrial valve manufacturers stand as discreet yet indispensable actors in plumbing.
They play a crucial role in ensuring the superior quality of industrial processes, whether in petrochemistry, energy production, food and beverage processing, or pharmaceuticals.
What Is an Industrial valve manufacturers?
An industrial valve is a mechanical device designed to regulate, isolate, or direct the flow of fluids, whether liquid, gas, vapor, or solid suspensions, within industrial processes.
Its fundamental role lies in the precise and controlled management of these fluids, thereby ensuring the proper functioning of industrial systems.
It generally consists of a body, a closure element, and an actuating mechanism. The choice of material and design of a valve is of paramount importance in ensuring its durability and reliability.
The operating conditions of a valve are also determining factors in ensuring its proper functioning.
Different Types of Industrial valve manufacturers
Ball Valve: A Technical Overview
Ball valves are essential in various industrial systems for precisely regulating fluids.
There are two types:
- Reduced bore
- Full bore, offering reduced pressure loss and facilitating pipeline cleaning.
These valves can be certified according to various standards such as ATEX, fire safety, or NACE, and are designed to minimize fugitive emissions.
Manufactured from various materials such as brass, bronze, cast iron, forged or cast steel, or forged or cast stainless steel, they offer adaptability to service conditions.
Connection options include threading, DIN or ANSI flanges, as well as SW or BW welding.
A feature of ball valves is their installation without constraints on specific flow directions, thus facilitating installation in industrial systems.
Connection options for ball valves are diverse:
- Threaded connection up to DN100
- DIN or ANSI flange connection, offering different configurations such as raised face RF, RTJ, or male or female socket
- Socket welding (SW) or butt welding (BW) connection.
A peculiarity of ball valves is that they generally do not have a specific flow direction, allowing for installation without constraints on the line.
- This flexibility simplifies installation and ensures increased convenience in industrial systems.
- The design of a ball valve depends on precise technical choices, suitable materials, and a variety of connection options to meet the specific needs of industrial applications.
Butterfly Valve
Butterfly valves, equipped with a single rotating disc, offer fluid flow regulation with minimal resistance, making them ideal for use in various industrial contexts.
Knife Gate Valve
Knife gate valves rely on a robust mechanism for effective isolation of networks, especially in conditions where the presence of suspended solids is high. Their sturdy structure minimizes pressure losses, ensuring smooth regulation of fluid flow.
Valve Selection Based on Function and Application
Valve selection is a critical aspect of engineering design, influenced by the function the valve needs to perform and the specific application requirements. Understanding the different types of valves and their advantages and disadvantages is essential for making informed decisions.
1. Function-based Valve Types:
Pushing Action Valves:
These valves operate by directly pushing the stopper onto the orifice seat. They include:
- Globe Valves: Known for their excellent shut-off and regulating characteristics but suffer from high-head loss.
- Rotating Action Valves:
These valves function by rotating the stopper. They include:
- Plug Valves: Quick acting with straight-through flow but have temperature limitations on certain types.
- Ball Valves: Provide quick shut-off with minimal leakage but may require attention to lubrication.
- Butterfly Valves: Offer quick operation and good flow control but may be bulky.
Sliding Action Valves:
These valves operate by sliding the stopper over the orifice face. They include:
- Gate Valves: Offer straight-through flow but are slower in operation and can be bulky.
Squeezing Action Valves:
These valves rely on squeezing action for operation. They include:
- Diaphragm Valves: Glandless and provide positive shut-off on dirty fluids but are limited by pressure and temperature.
2. Application-based Valve Selection:
- Isolation Function Valves: Gate, Ball, Butterfly, and Diaphragm Valves are commonly used for isolating sections of pipelines.
- Flow & Pressure Control Valves: Globe, Ball, Butterfly, and Diaphragm Valves are suitable for regulating flow and pressure within pipelines.
- Flow Reversal Prevention Valves: Check Valves are essential for preventing backflow in pipelines.
- Flow Diversion Valves: Ball, Plug, and Angle Valves are used for diverting flow between different pipelines or sections.
3. Considerations for Service Characteristics:
- Fluid Type: Identify whether the fluid is liquid, gas, steam, slurry, or solids, as this affects valve selection.
- Valve Applications: Consider the specific application requirements such as cleaning, slurry handling, hazardous fluid handling, etc.
- Pressure and Temperature Limitations: Choose valves rated for the maximum working pressure and temperature of the system.
- Operation and Maintenance Requirements: Factors such as fire resistance, operability, leak tightness, maintainability, and installation ease should be considered.
4. Cost Considerations:
- Valve costs vary based on type, material, and size. Gate valves are often cost-effective for certain applications, while butterfly valves may offer the lowest cost for specific conditions.
By considering both function and application requirements, engineers can select the most suitable valves to ensure optimal performance and reliability in industrial systems.
Informations about Sampling Valve Market: Growth Trends, Opportunities, and Forecas
Innovations and Trends in Industrial valve manufacturers
Technological advancements in the field of Industrial valve manufacturers open up new possibilities and push the boundaries of performance.
From automated systems and digital controls to sensor integration and IoT connectivity, these emerging technologies aim to improve operational efficiency and ensure cutting-edge solutions.
Industrial valves play a central role in regulating and controlling fluids in industrial processes. With a diverse range of valves incorporating the latest technologies, FAMAT SAMPLING is committed to providing tailored solutions to meet the specific needs of the pharmaceutical, food, cosmetic, biotechnological, and chemical industries.