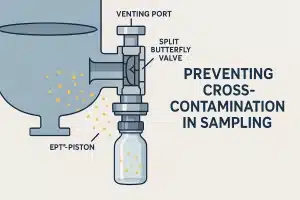
What is the Difference Between Gate Valve and Angle Valve?
Gate Valve vs Angle Valve serve similar functions in that they control the flow of fluids, but they differ significantly in design and applications.
1. Design and Structure
– Gate Valve: Gate valves operate by raising or lowering a gate to start or stop the flow. They are typically installed in straight pipelines, offering full flow when open.
– Angle Valve : Angle valves feature a 90-degree bend, directing flow in an L-shape and taking up less space, making them ideal for areas where piping cannot run in a straight line.
2. Flow Control Capability
– Gate Valve: Often used as an on/off device, gate valves are not ideal for regulating flow since they can cause turbulence when partially open.
– Angle Valve: Angle valves are more versatile and are better suited for applications requiring precise control, particularly when equipped with control mechanisms.
3. Ideal Use Cases
– Gate Valves: Common in applications requiring unobstructed flow, such as water distribution systems or systems with low flow control requirements.
– Angle Valves: Best for tight spaces and systems needing direction change or pressure control, often found in HVAC, plumbing, and chemical applications.
Understanding these differences can help you choose the right valve for your specific needs based on space limitations, flow requirements, and desired control.
Do I Need Angled or Straight Valves?
Choosing between angled and straight valves depends on your system layout and specific requirements.
1. Space Constraints
If your setup requires a directional change or is installed in a tight space, angle valves offer a compact solution. They eliminate the need for additional pipe fittings and rerouting, saving both space and installation costs.
2. Flow Requirements
For high-flow applications where straight-line flow is crucial, straight valves like gate or ball valves might be better suited. Straight valves provide minimal flow restriction and maintain consistent pressure.
3. Maintenance Needs
Angle valves allow for easier access during maintenance compared to straight valves, as they provide a clear point of entry. This can be especially useful in settings where regular maintenance is required.
4. Application-Specific Needs
Consider the type of fluid or gas in your system. Angle valves are often more adaptable to handling diverse media types, including high-pressure and corrosive substances. Straight valves may be ideal for simpler applications with low-to-moderate pressure and non-corrosive fluids.
By evaluating these factors, you can select the right valve type to ensure efficient operation, reliability, and ease of maintenance for your system.
How Long Do Angle Valves Last?
The longevity of angle valves depends on their material, usage frequency, maintenance, and the type of fluids or gases they control.
1. Material and Build Quality
High-quality angle valves made of durable materials, such as stainless steel or brass, tend to last longer than those made of less resilient materials. Valves exposed to corrosive fluids or harsh conditions should ideally be made from corrosion-resistant alloys.
2. Usage Frequency
In high-usage systems where angle valves are frequently adjusted, components may wear out faster. In such cases, investing in valves with reinforced seals and high-grade materials can reduce wear and extend lifespan.
3. Maintenance and Care
Routine maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of angle valves. Regular inspection, cleaning, lubrication, and timely replacement of seals or worn-out components help maintain optimal function and prevent breakdowns.
4. Expected Lifespan
Generally, a well-maintained angle valve can last anywhere from 5 to 10 years, with some high-grade valves extending beyond this range. For industrial applications where downtime is costly, considering the long-term durability of an angle valve is crucial when selecting a product.
Conclusion
Angle valves are invaluable components in industries requiring precise flow control, durability, and adaptability. By understanding their applications, types, and potential limitations, professionals in manufacturing, HVAC, and plumbing can make informed decisions about incorporating angle valves into their systems.
Although angle valves come with certain disadvantages, such as limited flow capacity and maintenance requirements, their space-saving design, precise control capabilities, and versatility make them suitable for a wide range of applications.
With the right material choice and regular upkeep, angle valves can serve as reliable, long-term solutions to enhance operational efficiency and control within industrial systems.
Selecting the right type of valve—angled or straight—depends on your system’s unique needs, space constraints, and fluid characteristics. By considering these factors, you’ll ensure that your valve choice supports a streamlined, efficient, and cost-effective setup, optimized for your facility’s specific demands.