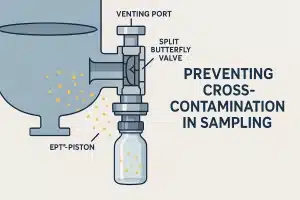
the flanged butterfly valve has emerged as a preferred option for its robustness and ease of maintenance.
In industries where the smooth, reliable control of fluid flow is essential—such as manufacturing, water treatment, and oil & gas—the choice of valve type can significantly impact operational efficiency, safety, and long-term cost.
Industrial Operations Managers like James Thompson face the complex task of selecting valves that not only meet stringent regulatory requirements but also deliver consistent performance under demanding conditions.
This guide provides a deep dive into the types, purpose, and operational differences of butterfly valves, with a focus on the flanged butterfly valve to assist you in making informed procurement decisions.
What Are the Three Types of Butterfly Valves?
Butterfly valves are a type of quarter-turn valve used in a wide range of industrial applications for their simplicity and effectiveness in controlling fluid flow. The main types of butterfly valves are:
1. Wafer Butterfly Valve
The wafer butterfly valve is one of the most common types and is designed for applications where a tight seal is necessary.
This valve type is held in place between two flanges and uses a series of bolts running through the pipe flanges and the valve body to maintain positioning.
Its main feature is that it prevents backflow in systems where reverse flow can cause contamination or process disruptions.
However, wafer valves generally have less robust sealing compared to flanged options.
2. Lug Butterfly Valve
A lug butterfly valve is similar to the wafer style but offers greater stability and sealing due to its “lug” design.
The valve is mounted using threaded inserts and bolts, which allow for easier maintenance since one side of the piping system can be disconnected without affecting the other.
This makes lug valves an ideal choice for applications requiring frequent maintenance or cleaning, as well as for scenarios where section-by-section repair is necessary.
3. Flanged Butterfly Valve
The flanged butterfly valve is notable for its durability and enhanced sealing, making it suitable for high-pressure environments. It features flanges on either side of the valve, which are bolted directly to the pipe flanges, ensuring a tight, secure fit.
This type is often preferred in heavy-duty applications because it provides a more stable connection and can handle higher pressure levels than wafer or lug designs.
Each type of butterfly valve serves distinct operational needs, and selecting the correct one can significantly improve system performance and safety.
The flanged butterfly valve, in particular, offers advantages for high-stakes applications where robust sealing and strength are paramount.
What is a Flanged Butterfly Valve?
A flanged butterfly valve is a type of valve designed with flanges on both ends, which are bolted onto the pipeline, forming a secure and leak-proof connection. Its primary purpose is to regulate or isolate flow within a piping system.
The valve consists of a circular disc or “butterfly” mounted on a rotating shaft, which is positioned in the flow path of the fluid.
By turning the disc, operators can control the flow, either restricting or allowing passage through the pipeline.
Key Features of a Flanged Butterfly Valve:
– Sturdy Connection: The flanges provide a strong attachment to the pipe, minimizing risks of detachment under high pressure.
– Leak Prevention: The flanged design offers enhanced sealing, making it ideal for critical applications where leaks would be problematic.
– Ease of Installation: Despite its robustness, the flanged butterfly valve is relatively easy to install and can be incorporated into various pipe setups.
– Wide Range of Applications: Commonly used in water treatment, chemical processing, and other industrial settings where flow control and durability are critical.
The design of a flanged butterfly valve ensures stability, reliability, and ease of maintenance, making it a versatile choice for industrial applications where regular upkeep is necessary to prevent system failures.
What is the Difference Between a Wafer and a Flanged Butterfly Valve?
Choosing between wafer and flanged butterfly valves depends on several factors, including operational pressure, maintenance needs, and installation environment. Here’s a breakdown of the main differences:
1. Connection Method
– Wafer Butterfly Valve: Held between two flanges with bolts, it lacks flanges of its own. This configuration is suitable for lower-pressure applications and offers a compact and lightweight option.
– Flanged Butterfly Valve: Features its own flanges, which are bolted directly to the pipe flanges. This creates a more stable, leak-proof connection, especially beneficial in high-pressure systems.
2. Sealing and Leak Resistance
– Wafer Valve: Provides basic sealing and is effective in preventing backflow in low- to medium-pressure applications.
– Flanged Valve: Offers superior leak resistance due to the flanged connection, making it the preferred choice for critical applications where fluid containment is essential.
3. Installation and Maintenance
– Wafer Valve: Easier to install and remove since it’s lighter and simpler to position. However, it may require additional support to maintain positioning in high-vibration settings.
– Flanged Valve: The bolted flanges add extra stability, making it easier to handle during high-pressure conditions and offering straightforward maintenance.
4. Application Suitability
– Wafer Valve: Ideal for applications that don’t require high-pressure resilience, such as low-pressure water distribution systems.
– Flanged Valve: Suited for heavy-duty applications where a robust, fail-safe connection is required, such as in water treatment plants, chemical processing, and oil refineries.
Each type has its strengths, with the wafer butterfly valve excelling in light-duty setups and the flanged butterfly valve standing out for applications requiring strength and high leak resistance.
Conclusion
Choosing the right valve type is a critical decision that impacts not only process efficiency but also long-term operational costs and safety. The flanged butterfly valve, with its durability and ease of maintenance, is an investment in stability and functionality—qualities highly valued in any industrial setting.